At a time when families and enterprises are actively moving towards energy self-susficient and low-carbon operation, solar energy systems are rapidly entering the public eye. But the most frequently asked by many users before installing the photovoltaic system is:
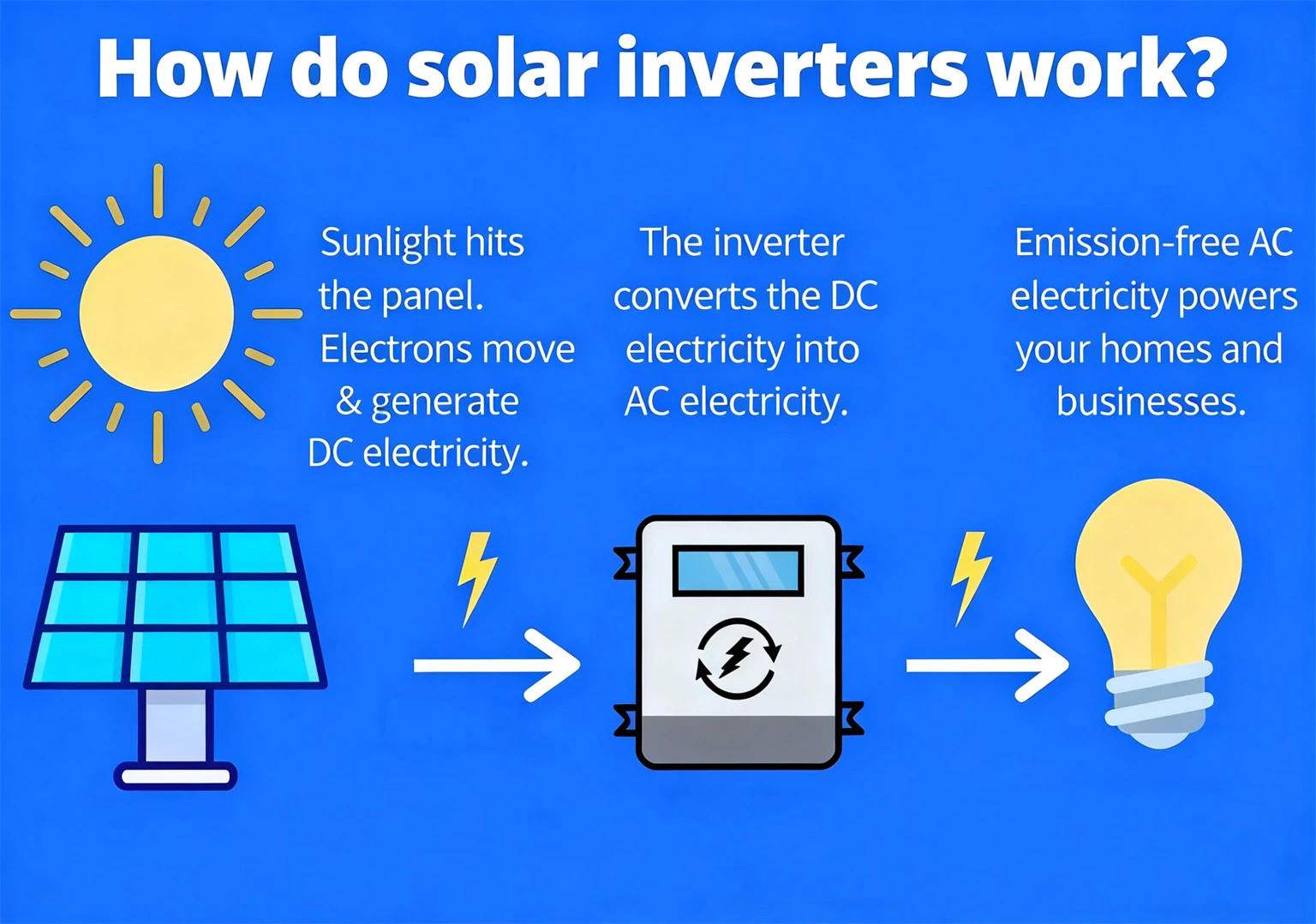
"What on earth does the solar inverter do?"
If the photovoltaic system is compared to the human body, solar panels are responsible for "absorbing energy", then the solar power inverter is the brain and heart of the system, which is responsible for converting solar energy into electricity that can be really used, and ensuring that the whole system is stable, safe and high effective operation.
This article will give you a comprehensive explanation in an easy-to-understand way:
- What is a solar inverter?
- How does it work?
- Why is it indispensable for both home and commercial use?
- How to choose the right inverter for you?
- Why will inverters become the core entrance of the energy system in the future?
Whether you are preparing to install solar energy or want to learn more about the photovoltaic system, this is a professional practical guide worth collecting.
I. What is a solar inverter?
A simple sentence:
Solar inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used at home.
It is also known as:
- PV inverter
- Solar energy inverter
- Photovoltaic inverter
- DC to AC solar converter
- Solar panel inverter
Why do solar systems need inverters?
Because:
- ✔ The electrical appliances at home are all AC.
- ✔ The output of the solar panel is DC.
- ✔ The missing "bridge" in the middle is the inverter.
Without an inverter, your solar system can only "generate electricity", but cannot really "use electricity".
A popular example:
Just like the mobile phone charger converts 220V AC into low-voltage direct current suitable for mobile phones;
And the work of the inverter is just the other way around: to turn the DC of the solar panel into the AC suitable for the power grid and the home.
II. How does the solar inverter work?
Although the internal structure is complex, the workflow of the inverter is actually very clear, which can be summarized into 5 steps:
- Receive direct current (DC) from solar panels
Solar panels generate electricity in the sun and output DC. - MPPT: Maximize power generation efficiency
The inverter has built-in MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking Technology), which automatically finds the best voltage and current of photovoltaic modules to maximize the power generation. - DC→AC Conversion: Core Steps
The inverter converts DC into sine wave AC through the internal circuit, so that electrical appliances can be used directly. - Synchronous operation with the power grid
For network-based and hybrid inverters, the inverter needs:
Synchronize with the frequency of the power grid
Match with the power grid voltage
Make sure that there will be no backfilling of power to the power grid (protect the power grid maintenance personnel) - Security protection and intelligent control
Modern inverters are equipped with:
Overvoltage/owervoltage protection
Prevent isolated islands
Overcurrent protection
AFCI arc protection
WiFi/APP remote monitoring
The inverter is not only "converting electrical energy", but also the intelligent control center of the system.
III. What is the use of solar inverter?
- Home and residential solar system
Providing clean electricity for families, spontaneous self-use + surplus electricity Internet access is the foundation of modern family energy independence.
✔ residential solar inverter
✔ solar grid inverter - Commercial and industrial photovoltaic projects
For example: factories, hotels, office buildings, etc.
Reduce electricity costs through spontaneous self-use, especially in high-energy-consuming scenarios.
✔ commercial solar inverter - Dis-gride system (area without municipal electricity)
Use off-grid inverters + battery energy storage in pastoral areas, islands, camps, remote mountainous areas, etc. - Photovoltaic + Energy Storage System
The inverter is equipped with an energy storage battery, which can achieve:
Storage of electricity during the day
Use at night
Automatic power supply in the time of power outage (UPS)
Hybrid inverters are the fastest growing products in the market at present. - Farm and agricultural applications
Solar water pumps, farm lighting and cold chain storage all rely on stable inverters.
IV. What are the types of inverters? Who is suitable for?
According to the application scenario, inverters can be divided into 4 categories.
- Grid-tied Inverter
The most common. Suitable for:
Have a stable power grid
I want to sell electricity to the power grid.
Household and commercial roofs
Advantages: high efficiency, moderate price, simple installation
Usage example: ordinary family roof + network - Off-grid Inverter
Suitable for:
Remote areas
Frequent power outages
Scenes that require battery energy storage
Advantages: Power supply can be provided even if the power grid is unstable - Hybrid Inverter
The most recommended "all-round" inverter.
Characteristics:
Grid-online + off-network
DC/AC two-way interaction
Support the hybrid management of batteries and photovoltaics
Suitable for wanting to achieve:
Spontante and self-use
Power outage emergency
Energy storage and utilization
Home users. - Micro-inverter
Each solar panel is equipped with a small inverter.
Suitable for:
The roof is often covered.
Components are in different directions.
Small roof project
Advantages: safe, flexible, higher power generation efficiency
But the price is usually higher than that of string inverters.
V. How to choose a suitable inverter?
The following are the parameter descriptions that users are most concerned about:
- Power size (kW)
The power of the inverter needs to be matched with the total power of the photovoltaic module.
Example: Family 3kW–10kW is the most common. - Conversion efficiency (the higher the better)
High-quality inverter efficiency ≥97.5%
The efficiency difference is 1%, and the annual power generation can be a few hundreds of degrees. - MPPT number of routes
Multi-MPPT can better cope with occlusion and multi-roofing situations.
Suggestions:
Household: 2-way MPPT
Commercial: 4–8 MPPT - Heat dissipation method
Natural heat dissipation: silent and long service life
Fan heat dissipation: commonly used in high-power equipment - Protection level (must-see for outdoor installation)
Outdoor inverter recommendation IP65+ - Intelligent monitoring
Support:
WiFi
App
Cloud monitoring
You can check the power generation, alarms and efficiency changes in real time.
Check out our recommended inverter products for home and commercial use
VI. Common problems and maintenance suggestions of solar inverters
The following are the most common questions for users:
- Why does the inverter overheat?
Possible reasons:
Poor ventilation
The ambient temperature is too high.
Dust blocks the heat dissipation
Running in excess of the rated power
Suggestion: Maintain good ventilation, and clean the shell and heat dissipation port regularly. - Why is the power generation declining?
Reason:
MPPT parameters do not match
The voltage of the board string is insufficient.
There is a cover
Aging of components
Poor line contact - How long is the life of the inverter?
The average life expectancy is 10–15 years. - How to extend the life of the inverter?
Avoid high temperature
Regular maintenance
Monitoring system
No overload operation
VII. The role of inverters in the future energy system
In the next 5–10 years, the inverter will become the energy management center.
- Mainstreamization of optical storage fusion (PV + Battery)
Hybrid inverters will become the standard configuration of home energy. - The rise of Smart Inverter
Equipped with:
Power grid interaction
Compensation for no work
High-frequency monitoring
Data analysis ability - Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
In the future, home inverters can be added to virtual power plants to achieve:
Sell electricity
Power grid scheduling
Get extra benefits - Charging and integration with new energy vehicles
Realize:
Direct charging of solar energy
Car Network Interaction (V2G)
On-board batteries participate in energy storage
Inverters will evolve from "power converters" to real "energy management centers".
VIII. How to choose a solar inverter that suits you?
- Home users: recommended hybrid inverter
Reason: It can be equipped with batteries, and the emergency power supply is more flexible. - The roof with a lot of cover: choose micro-reverse
It can avoid the power generation loss caused by shadow. - Commercial roof: select a string inverter
Stable, cost-effective and low maintenance cost. - Off-network scenario: choose high-power off-network inverter + lithium battery
Suitable for remote areas, rural areas, camps, etc.
Learn about the technical specifications and application scenarios of our many high-efficiency solar inverters
Solar inverters are the first step to energy independence.
A high-quality and correctly adapted solar power inverter not only allows you to "use solar power", but also determines the efficiency, safety and power generation income of the system.
Whether you are a home user, a business user, or preparing to enter the era of clean energy, understanding and choosing the right inverter is the first step towards energy freedom.





