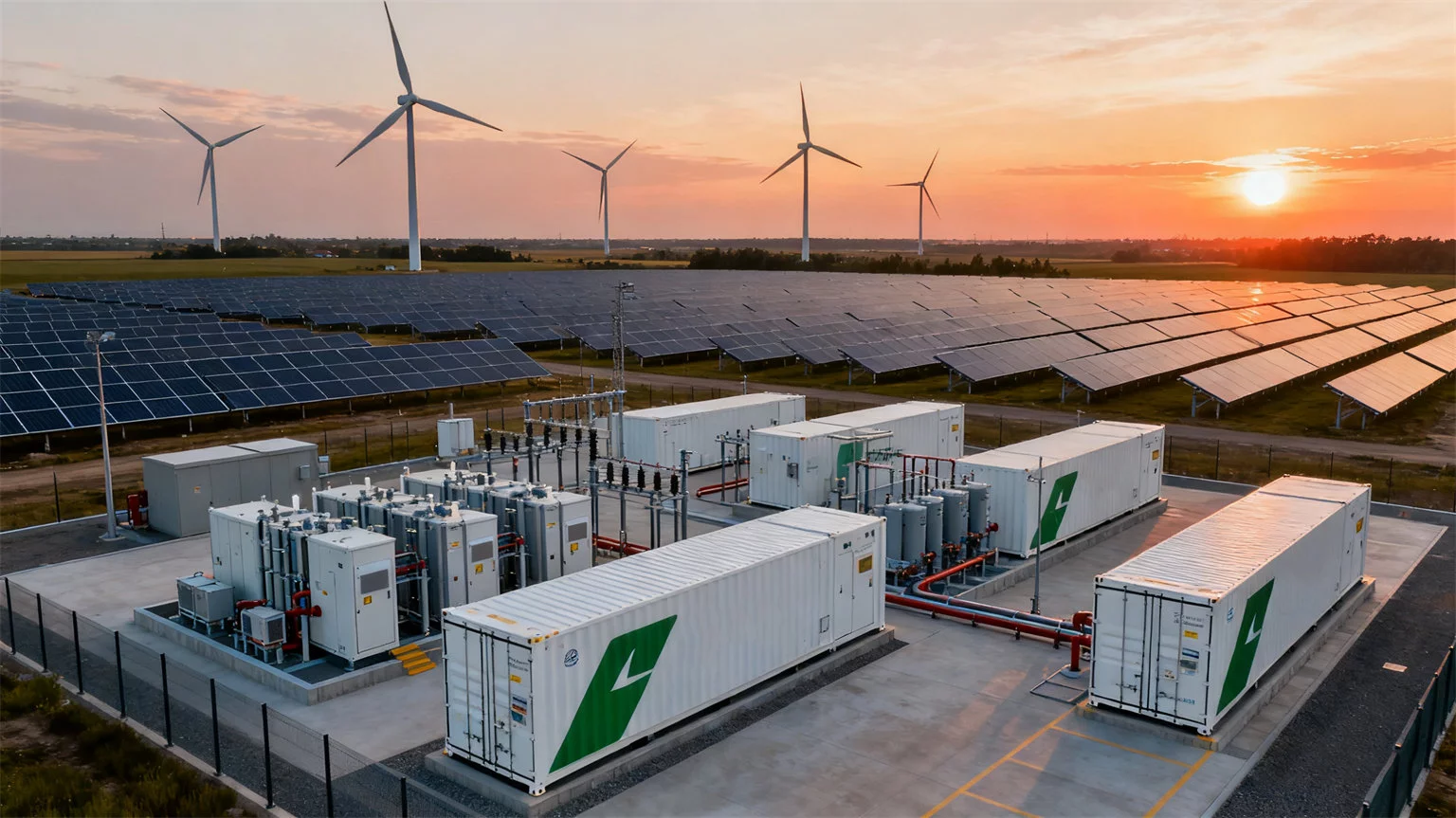
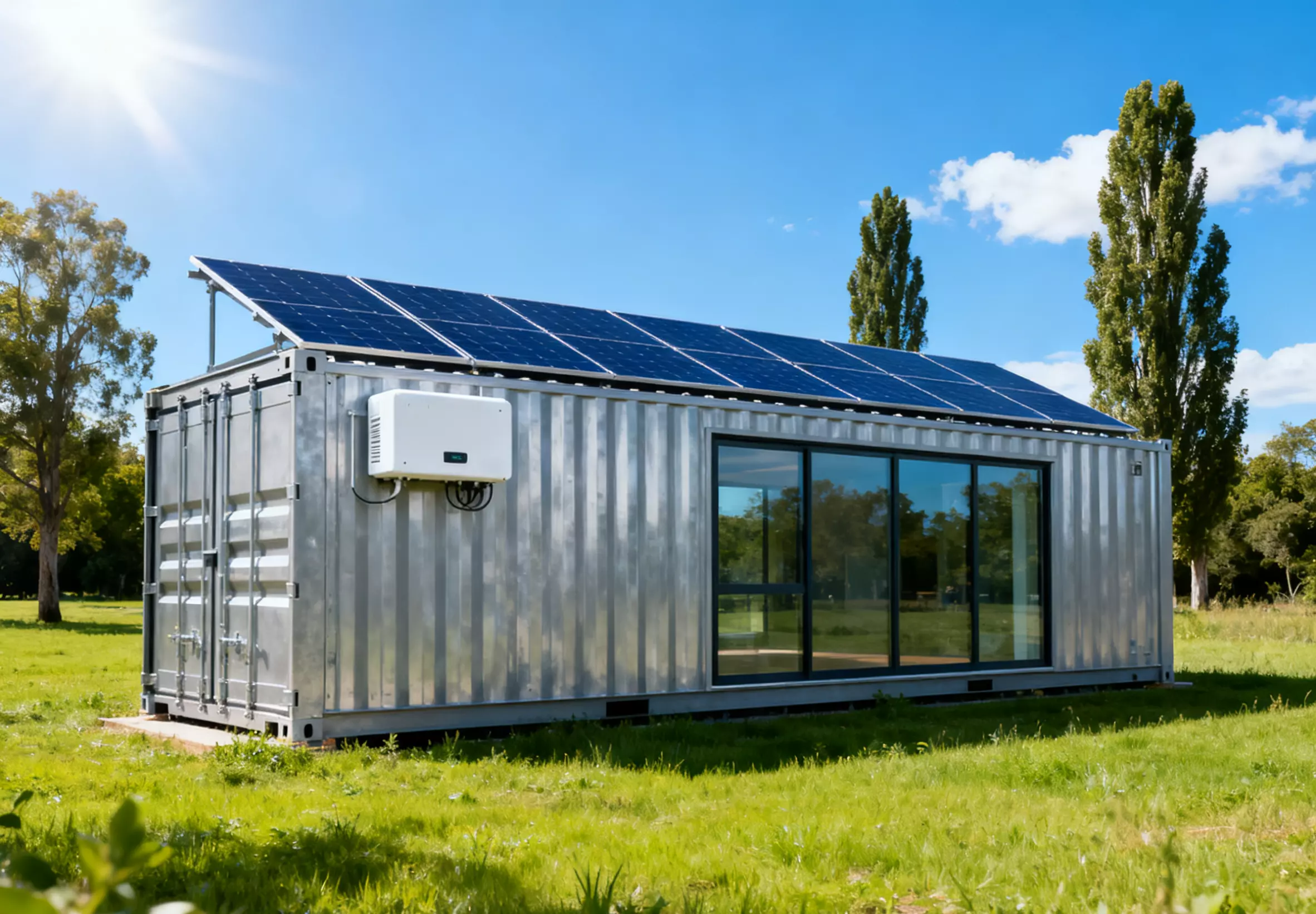
In today’s shift towards low-carbon energy systems, electricity storage inverters have become a core component of smart energy infrastructure.
As more homeowners and businesses adopt solar-plus-storage solutions, these devices ensure seamless, efficient, and flexible energy conversion between solar panels, battery banks, and the electrical grid.
This article breaks down what an electricity storage inverter is, how it works, key types, benefits, and why it is indispensable for the future of distributed energy.

What Is an Energy Storage Inverter?
An electricity storage inverter (also known as a battery inverter or hybrid inverter) is an advanced device that performs bidirectional energy conversion. It converts:
- DC to AC: Stored battery energy into usable alternating current for appliances or the grid.
- AC to DC: Grid or solar energy into direct current for battery charging.
More than just a converter, it also acts as the smart energy manager, enabling:
- On-grid and off-grid operation switching
- Smart battery charging/discharging
- Integration with solar PV, wind, and generator inputs
- Grid interaction for export, load shifting, or backup mode
How Does It Work? Step-by-Step
- Solar Input Conversion
DC electricity from solar panels is converted to AC for use in real time. - Battery Charging
Surplus energy not consumed immediately is sent to batteries via DC charging. - Discharging Power
When solar is unavailable (e.g., at night), stored energy is converted back to AC to run appliances. - Grid Interaction
In on-grid systems, the inverter may export excess energy to the grid or import during low-solar periods.
Many modern systems come with:
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
- Built-in EMS (Energy Management System)
- Remote monitoring via app or cloud platforms
- Smart load prioritization
Key Types of Energy Storage Inverters
| Type | Description | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Inverter | Combines solar and battery functionality in one unit | New solar-plus-storage installations |
| AC-Coupled Inverter | Connects to the AC side; ideal for adding batteries to existing PV systems | Retrofit systems or phased upgrades |
| DC-Coupled Inverter | Direct battery and PV connection at DC level, reducing conversion losses | High-efficiency new builds |
| Single vs. Three-Phase | Depends on building grid configuration (residential vs. industrial) | Residential (single), commercial/industrial (three-phase) |
Where Are Energy Storage Inverters Used?
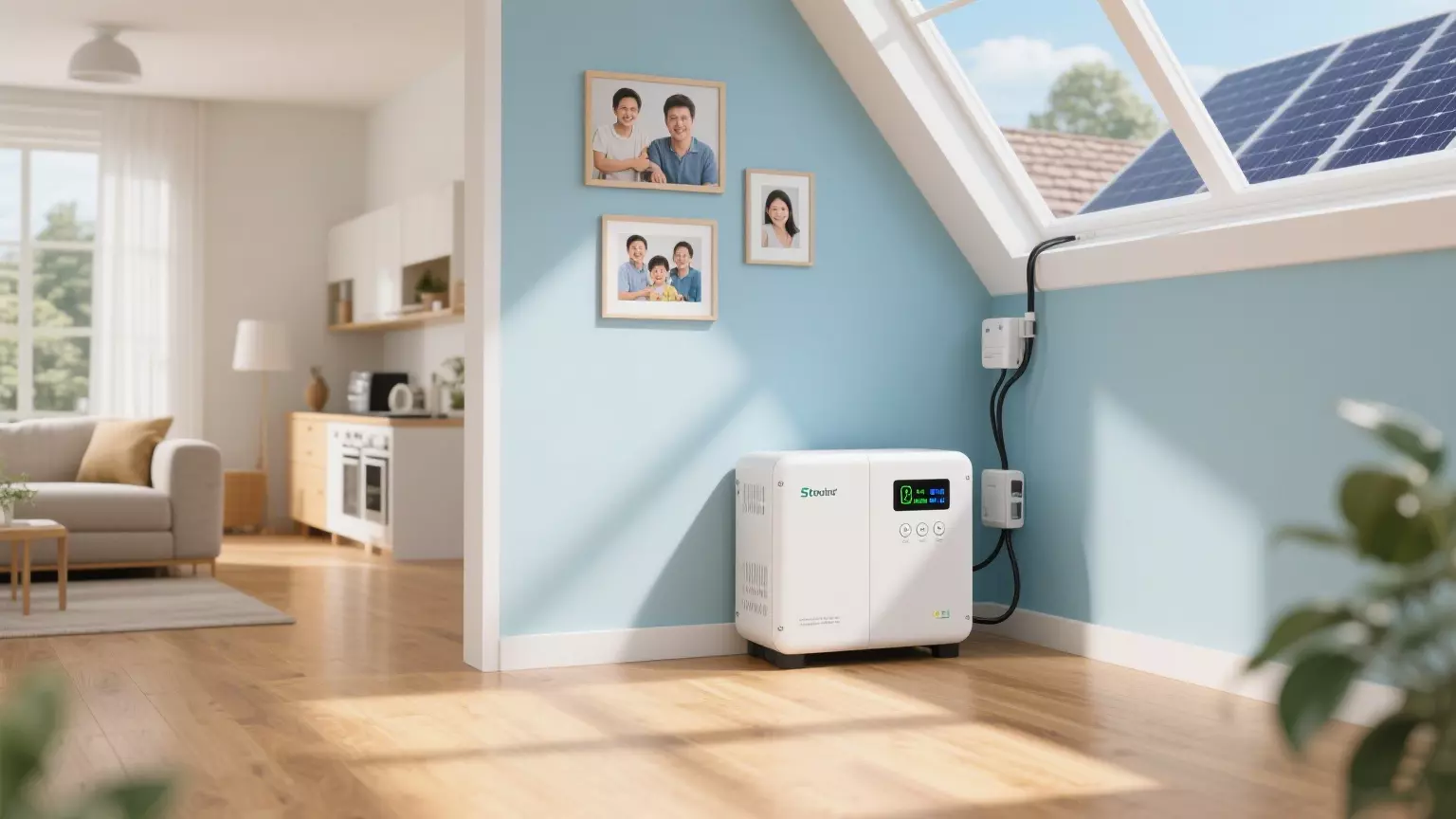

Residential Homes
Inverters paired with batteries supply energy autonomy and backup power. In states like California or Texas, households use these systems to ride through power outages caused by wildfires or storms.
Commercial & Industrial Facilities
Businesses integrate inverters for demand response, peak shaving, and reducing grid dependency. A factory may save thousands yearly by running on stored energy during peak hours.
Utility-Scale Storage
Projects like the Hornsdale Power Reserve in Australia deploy large-scale inverters to stabilize the grid with a 150MW/193MWh battery plant.
Why Are Energy Storage Inverters Important?
- Energy Independence: Reduce reliance on unstable grid power.
- Cost Optimization: Avoid peak electricity rates using stored energy.
- Backup Power Resilience: Maintain power during outages with off-grid capability.
- Grid Support Services: Provide voltage regulation and VPP participation.
- Maximize Solar ROI: Increase solar self-consumption and system value.
How to Choose the Right Energy Storage Inverter
- Compatibility: Support for lithium-ion, LFP, or lead-acid batteries.
- Capacity Matching: Size based on your load and battery system.
- Efficiency: Aim for ≥95% round-trip conversion efficiency.
- Modularity & Scalability: Allow future expansion or multiple units.
- Software Features: Load management, TOU scheduling, and app access.
- Warranty & Support: Choose trusted brands with solid service (e.g., SMA, Solaredge, Sungrow, Tesla Powerwall).
Future Trends in Energy Storage Inverters
- AI Optimization: Machine learning for smart energy control
- Grid-Forming Inverters: Support microgrids without centralized grids
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Turn EVs into mobile energy storage
- Higher Efficiency: Use of SiC and GaN for 98%+ conversion
- Modular All-in-One Systems: Integrated battery, inverter, EMS platforms
According to BloombergNEF, global energy storage capacity could exceed 400GW by 2030, with China alone deploying 35–56GW by 2025.
Conclusion: Smarter Power Starts with the Right Inverter
Energy storage inverters are more than just technical hardware—they’re the smart bridge that makes solar and storage systems effective, resilient, and economically viable. Whether you're a homeowner looking to save on power bills or a business optimizing energy use, choosing the right inverter is key to unlocking long-term value.